Part 6. Booleans
Booleans contain the values, true or false. It allows us to create conditions, which will enhance the decision making capabilities of the program.
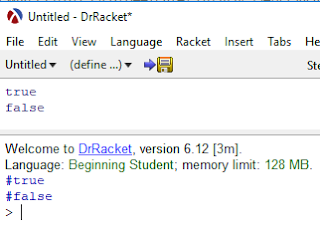
to define a boolean value in racket is simple
Since booleans are expressions themselves, these are the literal values. There are only 2 boolean functions, true or false.
The true power of booleans are revealed when we ask questions.
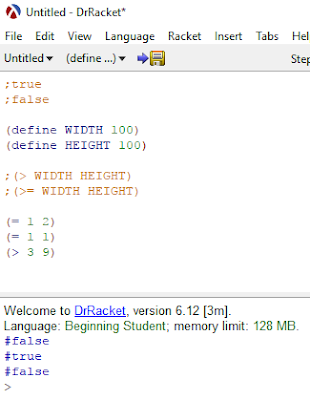
I have declared 2 constants, WIDTH and HEIGHT. Here, we used a new primitive called > which asks the question whether the first operand is greater than the second operand.
In this case 100 is not greater than 100, so it returns false.
There is another primitive called >= which asks if the left operand is greater than or equal to the second operand
in this case, the second part is true because 100 = 100.
Predicates are primitives that produce a boolean.
There are more predicates, go look them up.
There are string comparison operations
Image Properties can also be compared
If-Expressions in Racket are simple, there are 3 expressions.
(if <expression|Condition>
<expression|True>
<expression|False>)
As you can see, the first expression is the condition that would be evaluated, if true, the second expression would be executed, if false, the last expression would be executed.
Examples
This code would check if the image is tall or wide, in this code execution, you can see that it is tall. As you have observed, there is some black highlighting.
And this would be the result of I2
The second expression is evaluated when the answer is false.
There are rules for evaluating if-expressions
The AND predicate allows evaluating 2 or more predicate expressions, which outputs a true boolean if all predicate expressions are true. It resembles the Logical circuit AND.
Programming languages have OR and NOT predicates
Image Properties can also be compared
If-Expressions in Racket are simple, there are 3 expressions.
(if <expression|Condition>
<expression|True>
<expression|False>)
As you can see, the first expression is the condition that would be evaluated, if true, the second expression would be executed, if false, the last expression would be executed.
Examples
This code would check if the image is tall or wide, in this code execution, you can see that it is tall. As you have observed, there is some black highlighting.
And this would be the result of I2
The second expression is evaluated when the answer is false.
There are rules for evaluating if-expressions
- The question expression is evaluated, it must produce a boolean
- If the answer to the question expression is true, the next expression is evaluated
- If the answer is false, the last expression is evaluated.
- The resultant value of that expression is the value of the if-expression
The AND predicate allows evaluating 2 or more predicate expressions, which outputs a true boolean if all predicate expressions are true. It resembles the Logical circuit AND.
Programming languages have OR and NOT predicates
- OR - If one of the predicates are true, then the value is true
- NOT - Inverts the result of the predicate







Mga Komento
Mag-post ng isang Komento